|
|
|
|
Accessory nerve
02-09-2009
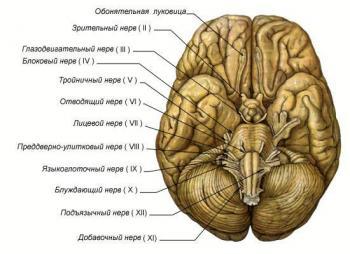 Accessory nerve
Accessory nerve motor. Spinal nucleus dobavochnogo nerve occurs in the lower section of the medulla oblongata, and gray matter of the spinal cord at the level of C1C5. Aksony these cells form a 6 – 7 rootlets, which extend to the lateral surface of the spinal cord and merge into a common trunk. Barrel accessory nerve enters the cavity Th
Turnip through the foramen magnum.
Spinal part of accessory nerve also contains efferent fibers from the cervical segments of the brain and spinal afferent fibers nodes received through
with front and rear mozgovymi spinal roots.
Cerebral part of the kernel are in the lower section of the medulla oblongata: anterior nucleus in the reticular formation, back behind the central canal. Fibers from these
nuclei come P5 spines between olive and the lower leg of the cerebellum.
Behind the cerebellar tonsils cerebral and spinal parts form a common trunk, which comes with a pair of X in the anterior jugular holes.
Coming out of the hole, additional nerve divides into two branches:
1) the inner branch consists mainly of fibers tserebralnoy part, goes to the vagus nerve and left him in the pharyngeal, laryngeal and cardiac branches;
2) the outer branch emerges from the cranial cavity through the jugular hole on the neck and innervates grudinoklyuchichnosostsevidnuyu and trapezius muscles. The functions of these muscles is to tilt the head sideways to turn a person in the opposite direction, lift under arm and acromion of the scapula upward, ie shrug, when conducting the scapula to the spine).
Symptoms defeat
The defeat of the nucleus, roots or trunk of accessory nerve is accompanied by the development of flaccid paralysis of the trapezius and sternal-klyuchichnosostsevidnoy muscles. The patient difficult to turn heads in a healthy way, at the patient side of the shoulder is omitted, limited lifting arms above the horizontal level.
During stimulation of cortical or subcortical structures may experience cramps in the form of tremors of the head in the opposite direction, or there is spastic
torticollis. Kernel accessory nerve has bilateral cortical innervation. Central paralysis of the trapezius muscle and grudinoklyuchichnosostsevidnoy can occur only when bilateral lesion korkovoyadernyh ways.
TRANSLATE FROM RUSSIAN BY GOOGLE
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Articles for theme “nerve”:
|
|
|
|
|
02-09-2009
Vagus nerve The vagus nerve is a mixed nerve. Innervates the organs of the neck, chest cavity, digestive tract, organs retroperitoneal space. Has the following core: three common core with nerve IX (nucl. alae cinegea, nucl. Ambiguus, nucl. Tgactus solitagius) and own parasympathetic nucleus nucl. dogsalis n. vagi. The vagus nerve contains motor, sensory and autonomic (parasympathetic) fibers. Motor fibers coming from the motor neurons of the dual-core to the striated muscle of the soft palate, pharynx, larynx and upper esophagus.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
02-09-2009
Glossopharyngeal nerve Pair of cranial nerves IX (p. glossophagyngeus) mixed nerve contains motor, sensory and parasympathetic (secretory) fiber, has 4 cores, which are located in the posterior part of the medulla oblongata. The double nucleus, nucl. ambiguus (in common with a pair of X), located in the middle part of the medulla oblongata, in front and lateral nucleus hypoglossal nerve. Axons of cells form the core motor branch of the glossopharyngeal nerve, which innervates the muscle only shiloglotochnuyu (ie stylopharingeus).
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
02-09-2009
Sluhovestibulyarny nerve Sluhovestibulyarny nerve sensitive nerve is the conductor of the special sensitivity of the organ of hearing and balance, and consists of 2x functionally different parts of the vestibular (pars vestibularis) and hearing (pars cochleagis). The auditory part (auditory nerve) provides transmission of sound stimuli. Sound waves are perceived by specific receptors spiral organ (Corti's). By petseptoram suitable peripheral processes of bipolar cells of the spiral node, located in the cochlea of the labyrinth.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
02-09-2009
An investigation of oculomotor muscles All oculomotor function are studied in the middle position of the head and look at the patient directly (primary position). Attention is drawn to the width of the eye slits of their value. Normally, the upper lid should not go to the area of the pupil. If it comes, it is ptosis (or poluptoz). To investigate the function of muscles, elevating the upper eyelid (for Burke), pressing the finger skin in eyebrows, asked to look up.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
02-09-2009
Abducens motor nerve, innervates the lateral rectus muscle eye. By connecting the branches in the trunk of the nerve included autonomic and sensory fibers. Abducens nucleus (nucl. abducens), which consists of large efferent nerve cells located in the tires (tegmentum) bridge at the bottom of the IV ventricle, near the middle line, more kperetsi. The trunk of the nerve leaves the brain at the posterior edge of the bridge between him and the pyramid of the medulla oblongata.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|