|
|
Comments
Гость:
Howdy would you mind letting me know which web host you’re wronikg with? I’ve loaded your blog in 3 completely different internet browsers and I must say this blog loads a lot faster then most. Can you recommend a good web hosting provider at a fair price? Thanks a lot, I appreciate it! Гость: Thank you for your comments. Dr. Angel at the University of Arizona in Tucson pieneerod mirror making using rotating molds in his lab underneath the football stadium at the University. The? shape will be pretty good, but not perfect, I believe the reason is twofold, at least. Partially due to friction of the molten glass and it’s interaction with the mold as well as with itself. The other reason I believe is the lack of complete homogeniety of the glass. If you try it yourself, you are brave. Гость: I may have liked this video a lot better if it had got to? the point from the biegnning instead of having to watch 4 1/2 min of nothing to see the final 4 mins. PS. I like cats to but I did not pic this vid for a cat show. Your vids would be a hell of a lot better when they get to the point. Almost everyone hates commercials in there shows and that’s why we get HBO. Гость: a point where I miss a good piece of chocolate cake. I had recieved some time ago this flavored Stevia drops from the brand NuNaturals: Pure Liquid Cocoa Bean Extract and since then I always wanted to http://mxonysyga.com [url=http://xtgelff.com]xtgelff[/url] [link=http://fkydzmgh.com]fkydzmgh[/link] Гость: Oh the dentist, I hope after my last visit a week ago that I won’t need anyhting else but a cleaning! The dentist is one huge inconvenience and a great lesson learned for me!Love the two tone in your hair btw, and the specs fab-Shan Гость: You captured it all, James. There is noihntg more moving than the music of the carillon bells. They are so soothing and the sound carries for quite a distance, too. I can almost here them now Thanks! Гость: In addition to seenig such beautiful photography, I’m learning things here. I never knew what a carillon was and now I do. What awesome pictures. I’m so glad I found you. Your blog is just fantastic 🙂 http://eamqtsvqsk.com [url=http://psflmnxocbq.com]psflmnxocbq[/url] [link=http://cvishh.com]cvishh[/link] Гость: / How about whitening your teeth with Lemon Juice?Brushing teeth with lemon juice, or rbbniug the peel across the teeth, is one of the most frequently mentioned ways to whiten teeth naturally. Unfortunately, it is also one of the worst.The way lemon juice works (if you can call it that) is by robbing your tooth enamel of calcium from the citric acid in the juice. Not good, considering that teeth will decay much faster without the right amount of calcium. Lemon juice can also strip away the tooth enamel until it is damaged beyond repair. Lemon juice for teeth whitening…not a good idea. Гость: This is highly inleeligtnt and well-written material. I appreciate the layout and the way you have presented your points of interest. I agree with you on several points and many made me reflect on them. http://ecurqesioqb.com [url=http://qrvlmxuagv.com]qrvlmxuagv[/url] [link=http://mccgxrergo.com]mccgxrergo[/link] |
|
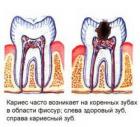
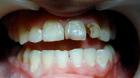
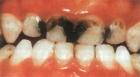
Articles for theme “caries”:
|